Digital Attack Surface – The Top 7 Vulnerabilities You Need to Know

The Modern Attack Surface is Digital and External
In the past, the attack surface was defined and protected by the boundaries of the organization’s physical network (aka the LAN). Using physical security methods, firewalls, and careful monitoring, organizations kept their data, endpoints, and networks secure. The entire attack surface was internal, within a well-defined and fortified perimeter.
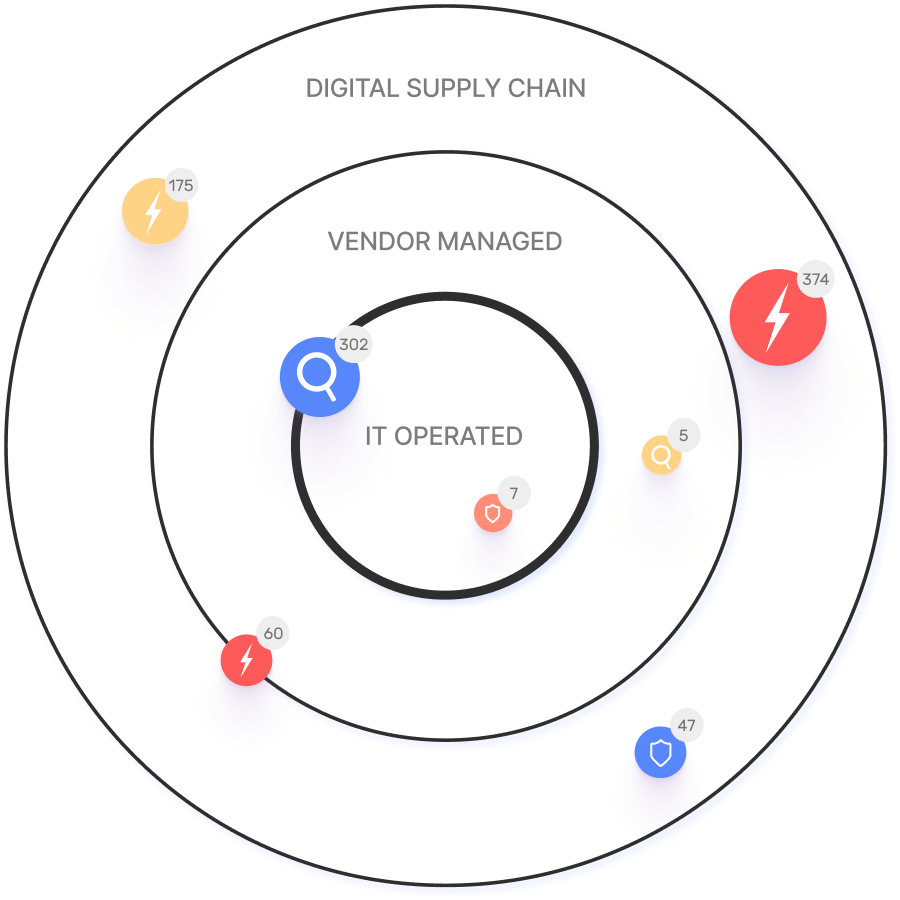
Today, interactions between employees, customers, and the organization are increasingly taking place online via web-based SaaS applications and cloud services. Such digital-transformation initiatives cause organizations to increase their online presence, multiplying the connections to external digital resources including cloud infrastructure, open-source software, and web applications from third-party vendors. The shift towards work-from-home (WFH) and hybrid work models is further distributing applications and data, and increasing internet exposure. For most organizations, the external attack surface, which comprises all internet-facing assets and connected digital supply chains, is now at least 3x larger than the internal one – and it is growing. Cyber teams need to expand their scope and protection with external attack surface visibility and mapping of third parties.
Common Cyber Risks and Vulnerabilities of the Digital Attack Surface
The digital attack surface, with its maze of interconnected online assets and sprawling digital supply chains, is a popular target for cyber criminals. As a result, new risks and vulnerabilities have taken center stage. Here are the seven most popular.
1. Cloud Misconfigurations
Public and private cloud environments offer a fast, simple, and inexpensive path for organizations to grow their digital infrastructure. Constantly adopting new Software as a Service (SaaS) offerings, organizations are willfully spreading their compute and data well beyond the reach of their own IT departments. While these “ex-IT” initiatives enhance business operations, the new cloud environments also give rise to new vulnerabilities.
Misconfiguration is the most common cloud-security vulnerability according to the National Security Agency. Even unsophisticated hackers are finding cloud misconfigurations attractive and relatively easy to exploit.
With their shared responsibility model, cloud service providers (CSPs) go only part way to providing adequate security services, leaving significant responsibilities up to their customers. Many such customers don’t know about or fail to follow cybersecurity best practices and inadvertently expose their data and credentials to attack.
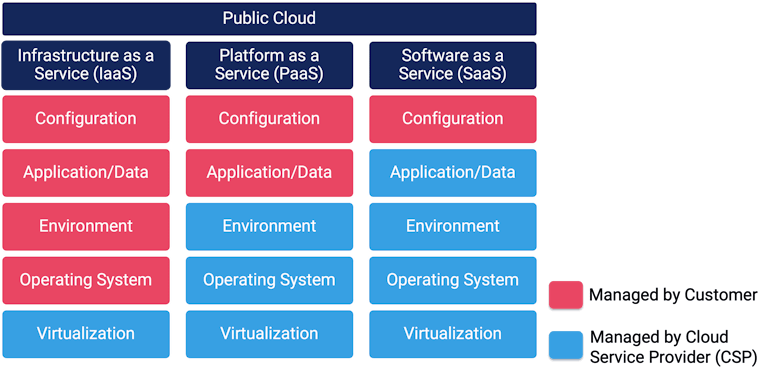
Furthermore, cloud architectures are not standardized. The three major public cloud providers, AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform, implement foundational cloud services differently. Customers who use more than one public cloud may be unaware of the differences and thus fail to apply the requisite security configurations across their multi- and hybrid clouds.
2. Access Control Out of Control
Inadequate restrictions and safeguards to prevent unauthorized access to cloud infrastructure can put the organization at risk. For example, unsecure cloud storage buckets can allow attackers to gain access to stored data.
The cloud providers have a track record of inadequate protection mechanisms. In its early days, top cloud provider, AWS, left S3 buckets completely open by default, inviting a plethora of data breaches!
While all the cloud providers have tightened their security over time, there are still myriad ways for attackers to find and exploit vulnerabilities. For example, weak authorization methods may enable attackers to elevate privileges and thereby gain access to sensitive data.
3. Web Applications and Third Parties
Many web applications manipulate sensitive personal and/or business data such as passwords, email addresses, and credit card numbers. Attracted by potential lucrative gains, attackers look for attack vectors that exploit web application vulnerabilities in order to exfiltrate data.
Today’s web applications share data with multiple, interconnected third-party services or systems. In turn, each of the third-party services may be interconnected with its own third-party services. Attackers pay close attention to these interfaces, seeking out potential vulnerabilities through SQL injections, authentication flaws, and privilege escalation – in your direct or indirect digital supply chain.
4. DNS Highjacking
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a central part of our online communications. Since the technology was created in an era when security wasn’t the top priority, it is inherently vulnerable to cyberattacks and needs special protection. The immense danger of highjacks lies in the central internet role that DNS plays.
Today, virtually every organization is exposed to multiple DNS servers in its digital supply chain. They are the weakest link in the chain. When a cybercriminal exploits a vulnerability to highjack the DNS server, he gains an ‘insider’ position of trust from which to launch any number of cyberattacks.
5. Email Server Takeover
Email is a trusted method of communication between the organization and its employees, customers, partners, and suppliers. Email is designed to allow people to send messages back and forth with little friction. It is this relatively open and free modus operandi that makes it so vulnerable to attack.
Since most companies use multiple internal and external email servers to route their daily communications, security requirements and configuration best practices vary greatly. Experienced cyber attackers are skilled at recognizing the email servers that are vulnerable to takeover. Once inside, they can easily ruin the organization’s reputation by launching a multitude of email-based phishing attacks against partners, suppliers, and customers.
6. Shadow IT
Shadow IT (a term defined in our glossary) is the term that defines the use of information technology systems, devices, software, applications, and services without explicit IT department knowledge and approval. In recent years, the growing adoption of “rogue” cloud services in organizations has made Shadow IT initiatives key targets for cybercriminals.
Any employee can create a public cloud account to quickly provision services and migrate workloads and data. But there is a price to pay. Non-IT-savvy employees who are not well-versed in security standards are prone to misconfiguring vital security options, leaving exploitable cloud vulnerabilities all over.
Since IT and security departments are oblivious to the “rogue” assets, they will be unaware of attempted and successful breaches until long after damage has been done.
7. Neglected and Unmanaged Assets
The speed with which business is conducted in the cloud and across supply chains often leaves behind the carnage of neglected assets and interconnections – easy pickings for cyber attackers. These can be authorized connections from enterprise applications to third-party suppliers who have been replaced. They can also be internal links to company IP or storage domains that have expired.
Many organizations still own servers, applications, and systems that no one has touched in months or even years. These unmanaged assets invariably run outdated software with known vulnerabilities that have never been patched – a veritable feast for the cybercriminal.
Digital Attack Surface Management and Protection
As the digital attack surface invariably continues to expand, so does the risk of cyberattack. To identify and prevent critical threats across the entire attack surface, you need effective External Attack Surface Management tools in your cybersecurity arsenal, to detect and assess vulnerabilities.
IONIX’s complimentary assessment of your organization’s external attack surface. You will gain visibility into your internet-facing assets and vulnerabilities that could pose a threat. Get a free risk assessment today.