Best Practices for Managing Cyber Risk

NIST National Vulnerability Database (NVD) includes a growing number of published CVEs annually, documenting a record 25,093 CVEs in 2022 — a 24.51% increase over 2021. Companies are facing more cyber risk than ever before, driven by widespread cloud adoption, the use of SaaS and APIs, and an increasing reliance on vendors.
The risk extends far beyond what you own; if a connected digital supply chain asset is at risk, so are you. Companies need a modern approach to managing cyber risk in today’s complex landscape.
What is Cyber Risk?
Cyber risk is the likelihood of experiencing these consequences due to a company’s information systems and security measures failing. In other words, cyber risk is the potential for data breaches or cyber attacks impacting a company’s information systems that may result in financial loss, reputation damage, and business disruption.
While definitions of cyber risk vary depending on what resource you consult, most definitions share the same core concepts. When a company’s information systems and security measures fail, there’s potential for sensitive data exposure to or access by unauthorized parties or malicious actors. Likewise, harmful consequences and loss may occur due to data breaches and cyber attacks.
What Contributes to Cyber Risk?
The Institute of Risk Management (IRM) defines three categories of cyber risk:
- Intentional security breaches are deliberate breaches carried out for espionage, extortion, or embarrassing the target company.
- Accidental security breaches are not malicious, yet they still result in sensitive data exposure, so it’s essential to address them.
- Operational IT risk exists because of poor system integrity and other factors.
Examples of Cyber Risk
Here are a few common examples of cyber risk:
- Weak passwords and improperly secured accounts, which could enable unauthorized access.
- Insider threats, such as disgruntled employees or spies.
- Software vulnerabilities, which open the door to potential malware.
- Cloud misconfigurations which open the door to threat actors
- The potential for social engineering attacks, which could enable cybercriminals to trick users into revealing sensitive information or allowing access to unauthorized users.
- Outdated or weakly secured communication protocols.
- Theft or loss of physical devices, especially unsecured devices.
- Insecure digital supply chains — subsidiary risk management has to cover all of the above.
For example, LocknCharge reports that lost or stolen devices cause 41% of data breaches. According to Zippia, 75% of employees use their personal devices for work purposes, yet just 32% of companies require employees to register their devices with IT and have security installed.
Just over half (51%) of employees say their companies have BYOD security policies. Companies that don’t take measures to ensure that employees’ personal devices are adequately secured face significant cyber risk.
How to Manage Cyber Risk
Let’s take a look at some of the most important best practices for cyber risk management.
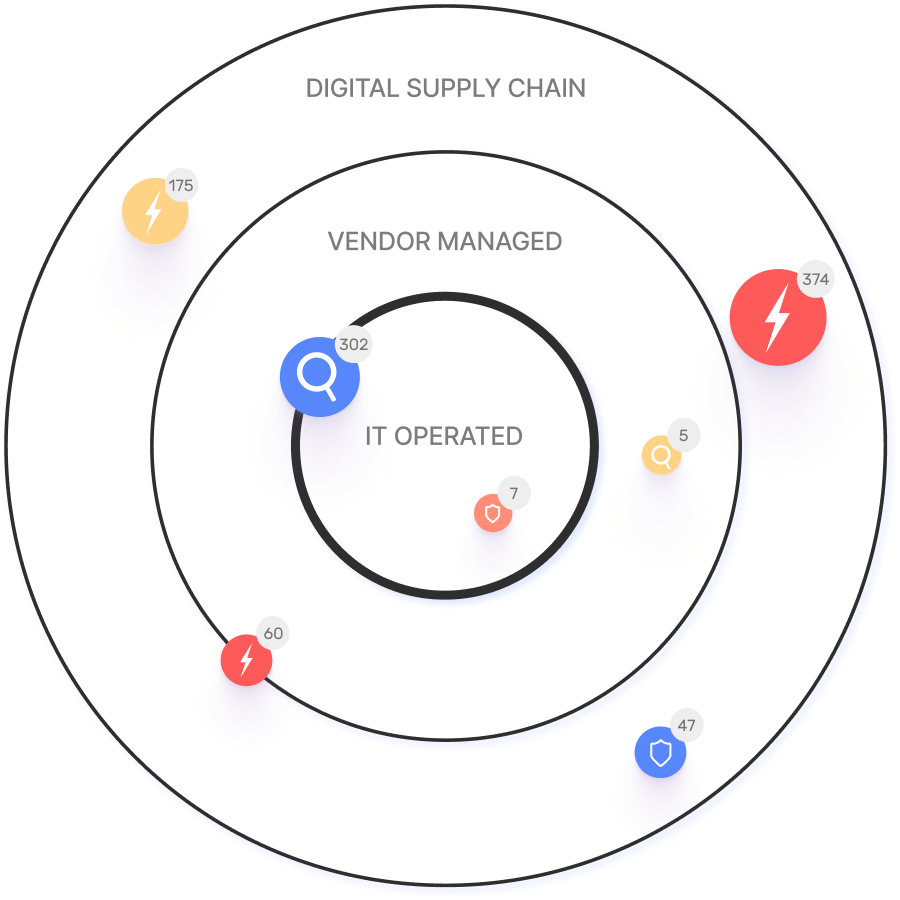
Gain supply chain visibility
Managing cyber risk starts with visibility into the attack surface. An external attack surface management (EASM) solution like IONIX streamlines this process by conducting a rigorous attack surface inventory, including:
- Domains and subdomains
- IP blocks
- Web applications
- Cloud environments
- Digital supply chains
- Public key infrastructure (PKI)
- DNS
Define your requirements and designate responsible parties
Cyber risk management aims to find the balance between what your organization needs and what the user wants. You must know your risk appetite, identify applicable legal and regulatory requirements, and designate responsible parties for cyber risk management.
Keep in mind that it’s not solely the IT/security department’s responsibility; everyone in the organization plays a crucial role in cyber risk management.
Understand cyber insurance coverage and policy requirements
Some cyber risks may be covered by your company’s cyber insurance policy. However, cyber insurers still require the insured party to implement appropriate risk reduction measures. Claims can be denied if the insured wasn’t complying with the minimum requirements when the breach occurred.
Conduct employee cybersecurity awareness training
Managing cyber risk is everyone’s responsibility, but many employees aren’t aware of the risks and what role they can play in mitigating them. Conduct comprehensive and ongoing employee cybersecurity awareness training to equip your team with the necessary knowledge and tools to play their part.
Deactivate or remove unnecessary devices and software
The more devices connected to the company network and the more software applications and services used, the greater the risk. Deactivate or eliminate software, devices, and accounts that are either redundant or no longer necessary to reduce the attack surface and reduce your cyber risk.
Develop an incident response plan
A survey conducted by Adastra found that 77% of business managers believe their companies are likely to experience a data breach within the next three years. The truth is that every company is at risk, and planning for when (not if) your business suffers a breach is vital.
Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines reporting requirements, remediation activities, roles and responsibilities, and communication procedures.
Assess your company’s cyber risk continuously
Your company’s cyber risk fluctuates daily as the attack surface expands and changes due to the shift to remote work due to COVID-19, the growth of shadow IT, and increasing cloud adoption, among other factors. That means you must assess your cyber risk continuously to discover previously unknown assets, their connections, and potential vulnerabilities.
Understand your attack surface
Mapping your attack surface provides visibility into the digital supply chain, but managing cyber risk doesn’t stop there. Identify your most valuable assets and their value to your organization.
Assess vulnerabilities and prioritize risk
Assess vulnerabilities impacting your company’s internet facing assets, their connected digital supply chains, and shadow IT. Identify and focus on exploitable risks first, and prioritize risks based on their potential impact and the asset’s value to your organization.
Manage Your Attack Surface and Digital Supply Chain Cyber Risk with IONIX
IONIX’s comprehensive EASM solution streamlines cyber risk management through automated asset discovery — including assets you didn’t know you had — for complete attack surface visibility.
IONIX continually analyzes asset risks and prioritizes risks based on connections, exploitability, and the potential impact of a breach, providing clear, actionable steps to accelerate mitigation and reduce cyber risk.
Learn more about effectively managing your organization’s cyber risk with IONIX by requesting a free attack surface scan today.