The Difference Between Authentication Bypass and Unauthorized Access
The nature of cybersecurity risk has evolved dramatically over time, challenging traditional approaches to security. Historically, organizations have concentrated their efforts on fortifying assets they directly own, assuming that this strategy provides sufficient protection. Unfortunately, this narrow focus fails to acknowledge a fundamental truth: attackers operate without regard for ownership boundaries.
Cyber attackers are opportunistic and adaptable, seeking out vulnerabilities wherever they may lie. They exploit weaknesses not only in internally owned assets but also in external entities interconnected with the organization’s ecosystem. This interconnectedness extends beyond physical boundaries to encompass digital supply chain connections, third-party services, and vendor platforms.
Authentication bypass and unauthorized access are prime examples of how attackers exploit these vulnerabilities. Regardless of ownership, attackers exploit weaknesses in authentication processes to gain illicit access to systems or resources. In this article, we explore these two vulnerability types, taking a closer look at their differences and their potential impact.
Authentication Bypass vs. Unauthorized Access
To gain a comprehensive understanding of cybersecurity risk, it’s vital to discern between authentication bypass and unauthorized access. While both present unique threats, grasping their subtleties is crucial for establishing effective security protocols.
What is an Authentication Bypass?
Authentication bypass involves exploiting vulnerabilities within the authentication process itself to gain access to protected resources without presenting valid credentials. Think of it as sneaking into a club through a broken window instead of going through the front entrance and getting your ID checked.
What are Some Examples of Authentication Bypass?
Attackers employ various methods, such as:
- Input Manipulation:
Attackers may tamper with input fields or parameters in the authentication mechanism to bypass credential requirements. For instance, they might inject malicious code or alter authentication tokens to deceive the system. - Exploiting Authentication Code Flaws:
Vulnerabilities or weaknesses in the authentication code can be exploited by attackers to bypass the authentication process entirely. This might involve leveraging buffer overflows, injection attacks, or other software vulnerabilities to execute unauthorized commands or access privileged information. - Use of Stolen Credentials:
In some instances, attackers may obtain valid credentials through illicit means like phishing, social engineering, or data breaches. By utilizing these stolen credentials, attackers can circumvent the authentication process and gain unauthorized entry to protected resources.
The repercussions of an authentication bypass vulnerability can be severe and extensive and can include:
- Data Theft: Unauthorized access to sensitive data can lead to its theft, manipulation, or exposure, resulting in financial losses, reputational harm, and regulatory penalties.
- System Disruption: Attackers may disrupt system operations by gaining unauthorized access to critical resources, altering configurations, or executing malicious commands, resulting in downtime, service interruptions, or operational disruptions.
- Malware Deployment: Once inside the system, attackers may deploy malicious software or malware payloads to further compromise security, spread across networks, or exploit additional vulnerabilities, exacerbating the impact of the breach.
What is Unauthorized Access?
On the other hand, unauthorized access focuses on gaining entry to a system or resource without the necessary permissions, even if valid credentials are used. Picture stealing someone’s key to enter their house, even though you have a similar key to your own.
What are Some Examples of Unauthorized Access?
Attackers achieve unauthorized access through methods like:
- Misuse of Legitimate Credentials:
Attackers may possess valid credentials but abuse them for unauthorized activities, such as accessing restricted areas, escalating privileges, or performing malicious actions beyond their intended scope. - Exploitation of Privilege Escalation Vulnerabilities:
Vulnerabilities within the system or application may enable attackers to escalate their privileges, granting them elevated access levels or administrative rights beyond what they are authorized to have. - Compromise of Weak or Default Credentials:
Attackers may exploit weak or default credentials, such as commonly used passwords or default usernames and passwords left unchanged by system administrators. By leveraging these credentials, attackers can gain unauthorized access to systems or resources and potentially escalate their privileges, posing significant security risks to the organization.
The effects of unauthorized access risk can include:
- Data Breaches:
Unauthorized access can result in unauthorized viewing, modification, or exfiltration of sensitive data, leading to breaches of confidentiality, privacy violations, and non-compliance with regulations. - Compromised System Integrity:
Unauthorized access by attackers can compromise system integrity by leading to the installation of backdoors or the establishment of a persistent presence. These breaches facilitate further exploitation, reconnaissance, or lateral movement within the network. - Erosion of Trust:
Unauthorized access undermines trust in the system’s security controls, eroding confidence among users, stakeholders, and partners, potentially resulting in lost business opportunities, customer attrition, or legal liabilities.
Key Differences
While both authentication bypass and unauthorized access pose significant security risks, three key differences set them apart:
- Authentication Mechanism:
Authentication bypass targets weaknesses in the verification process itself, while unauthorized access focuses on bypassing access controls once authentication is completed. - Credentials:
Authentication bypass often involves bypassing the need for credentials altogether, whereas unauthorized access may utilize valid credentials for nefarious purposes. - Intentionality:
Authentication bypass typically implies deliberate malicious intent, whereas unauthorized access can occur accidentally or intentionally.
Addressing Threats by Redefining Cybersecurity Paradigms
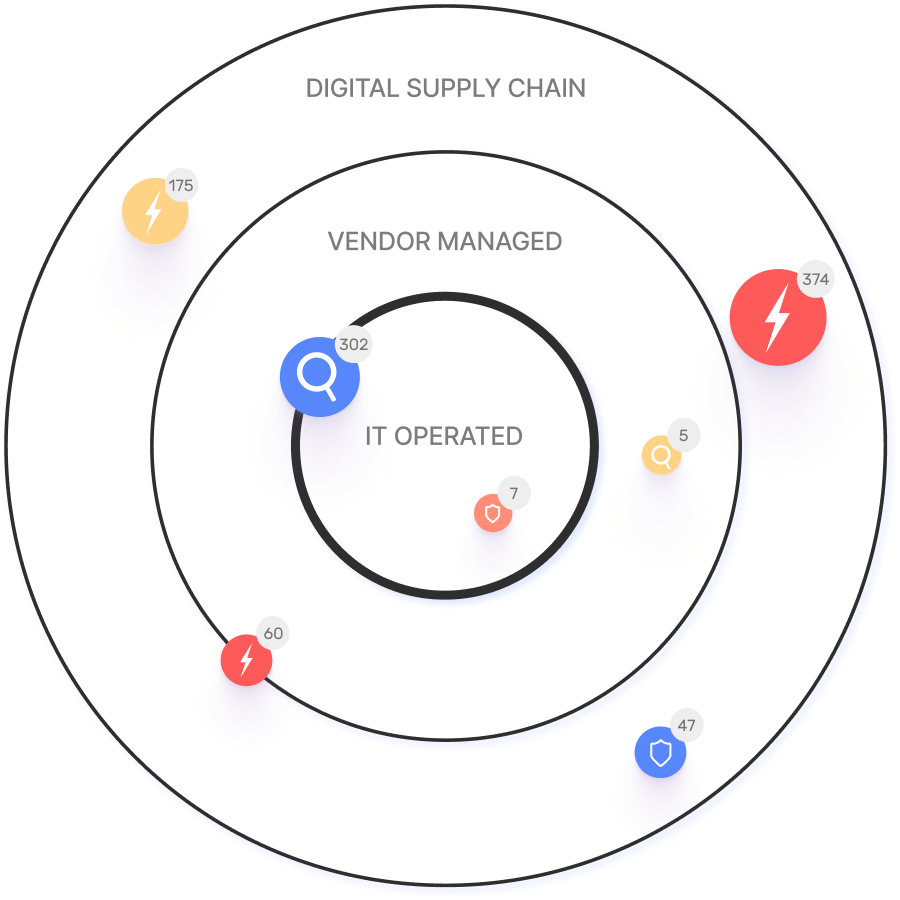
Today, the threat landscape facing most organizations has expanded significantly, leaving them vulnerable to security compromises from a broad range of vectors. According to IONIX research, 20% of exploitable attack surface risks stem from vulnerabilities within the digital supply chain. As businesses increasingly depend on third-party web services, vendors, and platforms, their digital supply chain expands, heightening their exposure to risk. This reality underscores the urgent need for a comprehensive cybersecurity approach capable of safeguarding not only internally owned assets but also those within the extended digital ecosystem from both authentication bypass and unauthorized access breaches.
IONIX distinguishes itself in the cybersecurity arena by offering a distinctive approach to exposure management. Central to its methodology is the acknowledgment that the interconnected nature of the digital supply chain necessitates a fundamental reevaluation of conventional security practices. Instead of exclusively focusing on internally owned assets, IONIX broadens its scope to encompass the extensive network of dependencies inherent in the digital supply chain.
At the core of IONIX’s effectiveness is its patented Connective Intelligence, an innovative technology that drives its Attack Surface Management (ASM) platform. Connective Intelligence empowers organizations to uncover their complete attack surface, including internet-facing assets and digital supply chain connections. By shedding light on these previously overlooked vulnerabilities, Connective Intelligence enables security teams to proactively identify and address risks before they can be exploited by malicious actors.
IONIX’s Innovative Approach to Mitigating Evolving Threats
As cybersecurity risks continue to evolve, organizations must adjust their security strategies to effectively counter threats from both authentication bypass and unauthorized access. By grasping the nuances between these vulnerabilities and understanding their potential impact, organizations can deploy robust security measures to safeguard their digital assets and bolster resilience against evolving cyber threats.
IONIX’s cybersecurity approach revolutionizes conventional paradigms by recognizing the interconnected nature of the digital supply chain and expanding the scope of ASM tools. Powered by innovative Connective Intelligence technology, the IONIX ASM Platform enables organizations to uncover their entire attack surface, proactively identifying and addressing vulnerabilities before they become serious threats.
By embracing a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy and harnessing advanced technologies like Connective Intelligence, organizations can fortify their digital ecosystem against authentication bypass, unauthorized access, and other emerging threats in today’s dynamic threat landscape.